Authors: Said Al Rabadi , Akl Awwad
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48103/jjeci4122021
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 96-105
Abstract
Jordanian sand deposits are naturally available in enormous amounts, located in Sweileh area, West Amman, which are mainly composed of low costs constituents from silica, Kaolin Clay, and metal oxides. A novel and simple methodology is presented for preparation, characterization, and behavior assessment of the potential nano-Kaolinite/ Silica oxides composites (nKSOC), for the immobilization of heavy Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions’ discharges. In this study, the synthesis of nKSOC
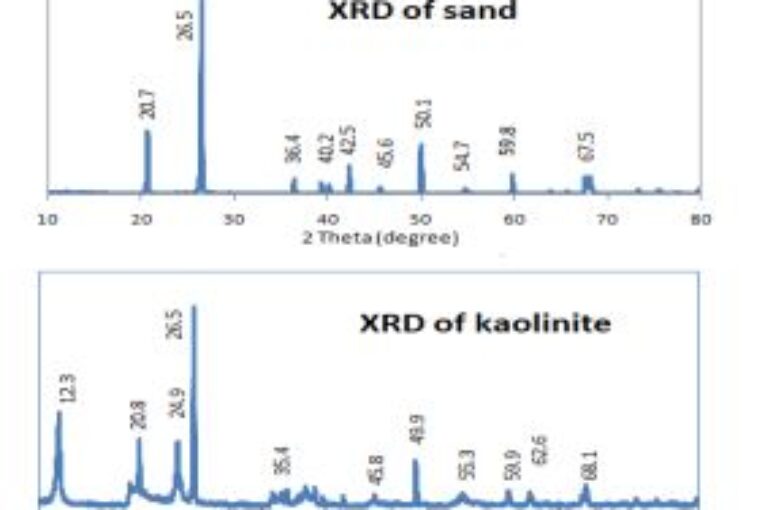
composites was conducted from the Jordanian sand deposits, mechanically reduced in size and then chemically acid-activated at room temperature, for the scope of wastewater purification through adsorption of heavy Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from an aqueous medium. The synthesized nKSOC were subjected to analytical techniques; X-ray diffraction (XRD) and size reduction, to deduce their appropriate characterizations. Key parameters, considered for the enhancement of the adsorption technique,
were pH, initial metal ions concentration, contact time, sorbent’s dosage, and temperature. Experimental data were analyzed by Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models, for the prediction of the adsorption behavior. Langmuir isotherms reproduce the experimental data with a maximum adsorption capacity of 172.4 (mg/gadsorbent) and 158.7 (mg/gadsorbent) for Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions,
respectively, under unchangeable conditions of the constant temperature of 303K and slightly acidic pH in the range of 5.5 – 6. The adsorption of heavy metal ions was spontaneous and endothermic; (∆Ho
) (7.47 kJ/mol) and 7.87 (kJ/mol) for Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, respectively, and with negative Gibbs free energy (∆Go), the adsorption process is performed under mild conditions.
In virtue of these remarkable findings, nKSOC could be effectively used as a low-prized adsorbent to uptake heavy Pb(II) and Cd (II) metals from aqueous waste media.
Paper type: Research paper
Keywords: Sand deposits, nano-Kaolinite/Silica oxides composites, adsorption isotherms, heavy metals, thermodynamics. Citation: Al Rabadi S., and, A., Awwad “Immobilization of heavy Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous discharges”, Jordanian Journal of Engineering and Chemical Industries, Vol. 4, No.3, pp:96-105 (2021).