Authors: Ibrahim Suleiman, Niveen Assaf, Michael Stockenhuber, Eric M Kennedy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48103/jjeci452021
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 38-43
Abstract
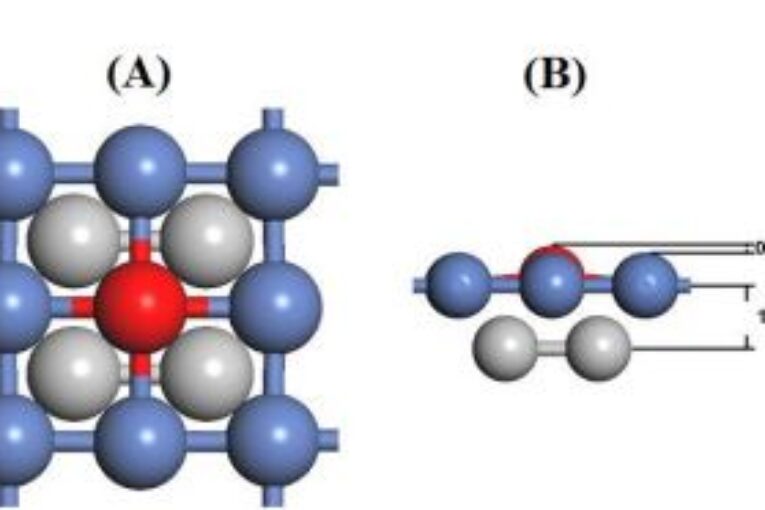
The mechanism of methane dissociation on an Rh-decorated Ni(100) surface has been investigated Using density functional theory. The study includes the determination of the most stable adsorbate/adsorbent configurations of the species associated with subsequent reactions and generating the energy surface for 𝐶𝐻4 dissociation process. The Rhdecorated Ni(100) surface was found to be more favorable for the process than the NiRh(111) configuration, mainly due to lower the activation energy of 𝐶𝐻 decomposition reaction by 48.5%, leading to a higher conversion of 𝐶𝐻4 to carbon and hydrogen
Paper type: Research paper
Keywords: DFT; methane; dehydrogenation; cracking
Citation: Ibrahim Suleiman, Niveen Assaf, Michael Stockenhuber, and Eric M Kennedy “Methane dissociation over the Rh-Decorated Ni(100) Surface: A density functional theory investigation” Jordanian Journal of Engineering and Chemical Industries, Vol. 4, No.2, pp:38-43 (2021).