Authors: Naser Almanaseer
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48103/jjeci332020
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 19-27
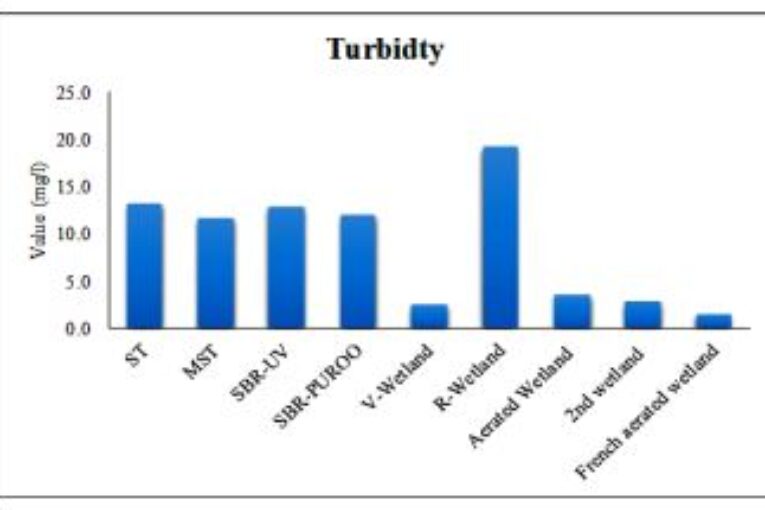
The nine different technologies are constructed at the pilot scale in one experimental site at Al-Balqa Applied University and use the same wastewater characteristics as the inlet. Monthly samples were collected from the inlet and outlet of nine different decentralized wastewater treatment technologies for three years (June 2016-June 2019). The samples were analyzed for physical, chemical, and biological parameters including TSS, Turbidity, pH, COD, DO, NH4, NO3, TN, BOD, and E. coli. Removal efficiencies for the nine technologies are obtained for COD, BOD,
TN, and TSS to be above 95%. NH4 the removal efficiencies for the nine technologies vary and found to be in the range of 27 to 76% while for the E. coli in the range of 65 to 95%. Further, data on energy consumption were collected for each technology and found for the nine investigated technologies in the range of 0.03 to 0.30 Jordan Dinars per treated cubic meter. The investigated technologies were evaluated, and the best options were endorsed.
It is concluded that the adaptation of decentralized wastewater treatment will certainly help protect the hydrologicsystem in Jordan especially in the high lands where significant groundwater recharge occurs and a considerable amount of surface water flows towards Jordan Valley and collection dams.
Keywords: Wastewater, decentralized wastewater treatment, contamination, pollution, innovative technologies, removal efficiency