Authors: Mohamad Ibrahim
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48103/jjeci172018
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 84-92
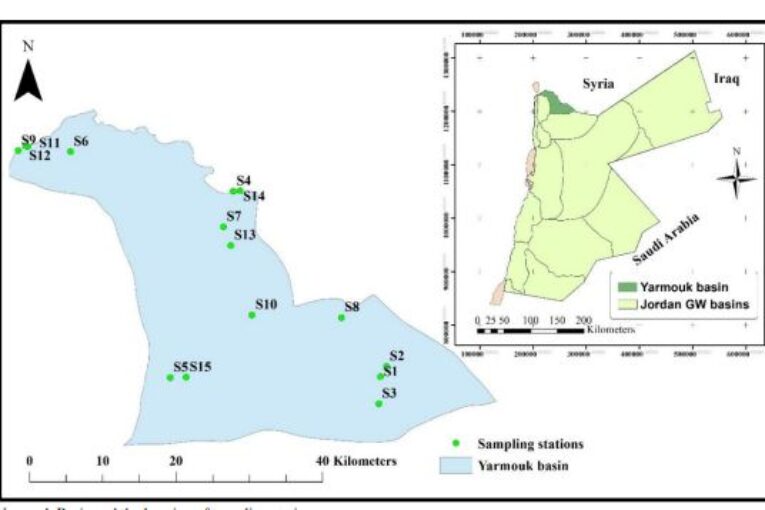
Groundwater quality is an issue of national concern in Jordan since it is the main water source for drinking, agriculture andindustrial purposes. In this context, an attempt has been made to determine the suitability of groundwater in the Yarmouk Basin in Jordan for drinking purposes using the weighted arithmetic water quality index approach with the respect to the Jordanian standards for drinking water. Groundwater quality records from 15 sampling stations spread across Yarmouk Basin during 2008-
2015 are used. Seven physical and chemical parameters are selected to calculate the water quality index. These parameters are pH, total dissolved solids, total hardness, sulfates (SO4 −2 ), chlorides (Cl−), nitrates (NO3−), and sodium (Na+). The relationship between the selected groundwater quality parameters is evaluated using the correlation coefficient. A strong relationship is found between several parameters such as Cl− with Na+, total dissolved solids with Na+, Cl−
, TH and SO4−2 and total hardness with SO4−2.A moderate relationship is found between SO4−2 with Na+, TH with Cl− and Na+, SO4−2 with Cl−, Cl− with NO3− and NO3− with Na+
.Also, the mean concentration values of the physical and chemical parameters are almost below the maximum allowable level based on Jordanian standards for drinking except for two sampling locations. According to water quality index scale classification, the groundwater quality of the studied locations is in the excellent to poor water range with computed mean water quality index
values range from 26.3 to 107.93. Out of 15 studied locations, ten locations are classified in the ‘Excellent water’ class, fourlocations as a “Good water” class, one as a “Poor water” class. None of the studied locations are classified in the “Very poor water”
class and “Water unsuitable for drinking purpose” class. Temporal variations and spatial distribution of groundwater quality in Yarmouk Basin based on WQI are also evaluated. The WQI spatial distribution map clearly showed the best locations for drinkingwater in the Yarmouk Basin. Water quality indices are used to provide theoretical support to water managers and policymakers for
proper actions on groundwater quality management.
Keywords: Water quality index, groundwater quality, drinking water, spatial distribution, hydrochemistry, Yarmouk basin

![Different Polyoxometalate Structures Obtained from the Na11H[H(2-x)Bi2W20O70(HWO3)x]·46H2O(x=1.4).](https://jjeci.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/111244-165x109.jpg)