Authors: Haider Hadi
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48103/jjeci382020
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 64-72
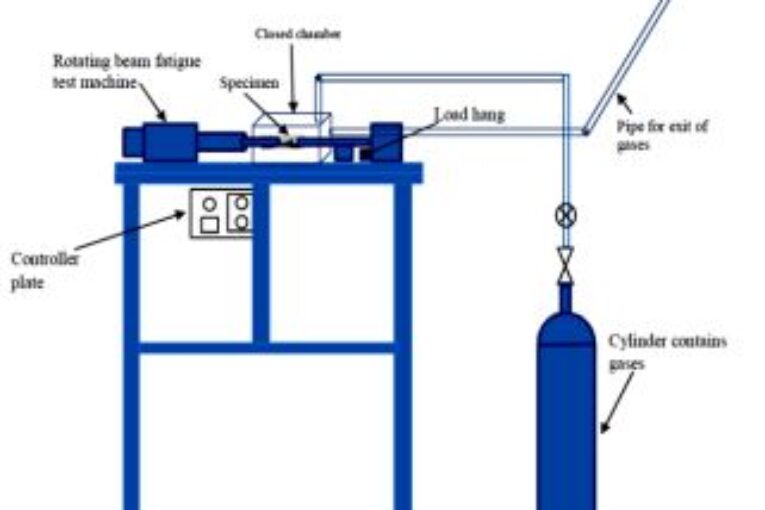
The fatigue limit and lifetime of epoxy-based coatings may be affected by various factors, especially the environmental effects. This paper evaluates the impact of air, potable water media, and pollution gases (CO2, H2S, and SO2) on the fatigue performance of two types of epoxy-based coatings (polyamine and polyamide epoxy-based coatings) used as lining for potable water storage tanks. The fatigue test apparatus is assembled in the laboratory and utilized for testing. Different factors are discussed, including absorption, adsorption, and the reaction of environmental gasses with
polyamine and polyamide coating surfaces. The influence of porosity on the epoxy-based coatings is experimentally determined, and its effects on fatigue limit and fatigue life are discussed in detail. As a result, the coatings were applied to improve the fatigue resistance of stainless steel. The fatigue limits of both types of coatings tested in potable water are lower than the value obtained when tested in air or gas environments. The fatigue limit of polyamine coating is greater
than the polyamide coating. The microscopic inspection indicated a different mechanism for initiating fatigue crack, and the test environments are affected by the nature of the fracture surface.
Keywords: epoxy coating; fatigue limit; diffusion; porosity; AISI 316 steel