Authors: Al-Mazaideh Ghassab
DOI: 10.48103/jjeci432021
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 24-30
Abstract
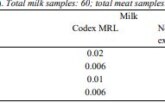
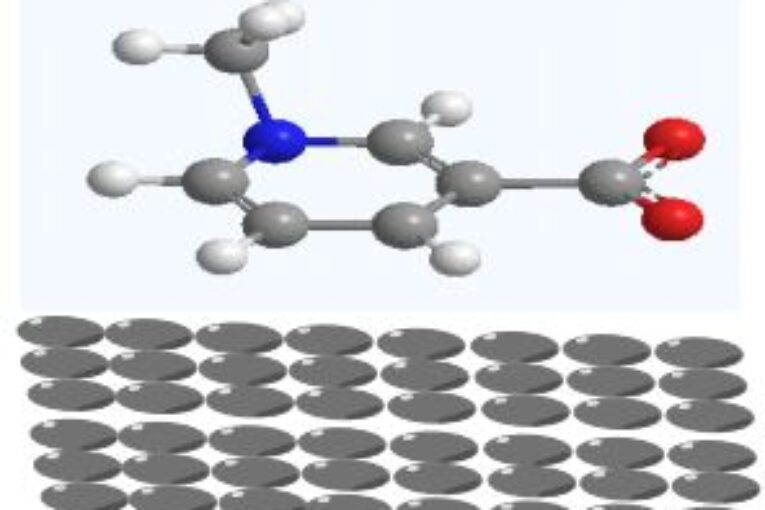
DFT calculations were carried out on significant Fenugreek seed compounds (1-Methylpyridinium-3-carboxylate MPC, Apigenin-8-C-glucose ACG, and 2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine IBMP) as a green source of ecologically friendly Fe, Al, and Cu metal corrosion inhibitors. Complete geometry optimizations were performed by DFT-B3LYP/6-31G* to determine any relationship between the chemical structure and corrosion inhibition, mostly on metals’ surfaces. Global computational parameters of the inhibitors and thermodynamic Gibbs process of adsorption of metals were calculated and used to evaluate each corrosion inhibitor’s performance. Our findings showed that MPC has the maximum anti-corrosion
efficiency across all molecules with a physical adsorption mechanism. It exhibited significant inhibition efficiency with Cu when compared with Fe and Al, based on the highest electrophilicity index (ω) values compared to other inhibitors and its impact on metals in the following manner: Cu>Fe>Al. In regards, the range of inhibitors increased by the following order: IBMP>ACG>MPC. Remarkable corrosion inhibition of MPC is demonstrated by its unique high electrophilicity, softness (σ), and lowest ∆Egap on the metal surface. These outcomes are close to the experimental work.
Paper type: Research paper
Keywords: MPC, DFT, green inhibitors, Fenugreek seed, metals.
Citation: Al-Mazaideh G.” Phytoconstituents of Methanolic Extract of Fenugreek seeds as a green corrosion inhibitor of metals (Fe, Al and Cu)”
Jordanian Journal of Engineering and Chemical Industries, Vol. 4, No.1, pp:24-30 (2021).