Authors: Mohammad Khanfar, Taleen Kopti, Natalie Gharaibeh, Ziad Abu El-Rub
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48103/jjeci492021
JORDANIAN JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING AND CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES (JJECI)
Pages: 70-77
Abstract
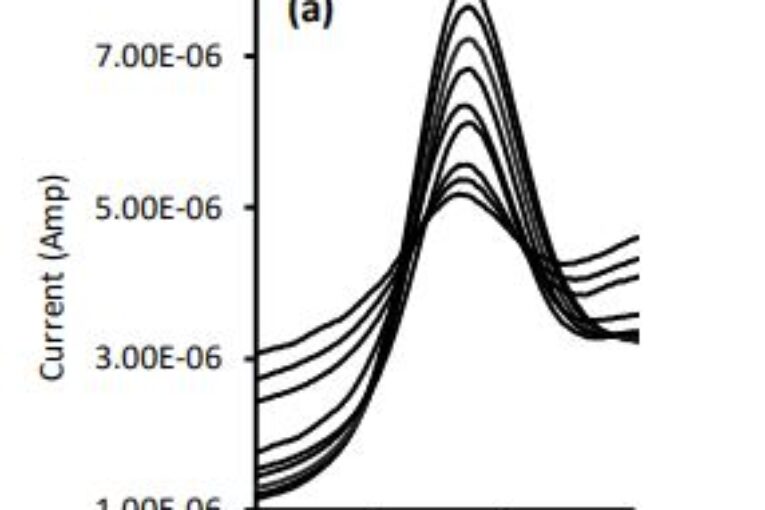
This study aims to compare differential pulse voltammetry as a tracking method with chromatography and photometry. The three methods were used to track the degradation of the model compound hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) where 250ml of 0.50mM HCT solution (pH of 3.50 and ionic strength of 0.010M) was electrolyzed with 50.0mAmp constant current. The degradation process
demonstrated great fit (R2 >0.99) with pseudo-first-order kinetics when the three tracking methods were utilized. However, different rate constants were reported for these methods: 0.032min-1 , 0.016 min-1
, and 0.0052min-1 for the chromatographic, photometric, and
voltammetric techniques, respectively. The observed variation was attributed to the nature of the utilized probing methods. The differential pulse voltammetry is promising as an electrolytic decomposition tracking method; however, the working probe to target pollutants needs to be improved.
Paper type: Research paper
Keywords: Anodic oxidation, differential pulse voltammetry, hydrochlorothiazide, electrolytic degradation.
Citation: Khanfar, M., T., Kopti, N., Gharaibeh, and Z. Abu El-Rub “Differential Pulse Voltammetry as an Alternative Method for Tracking Hydrochlorothiazide Electrolytic Degradation”, Jordanian Journal of Engineering and Chemical Industries, Vol. 4, No.3, pp:70-77 (2021)